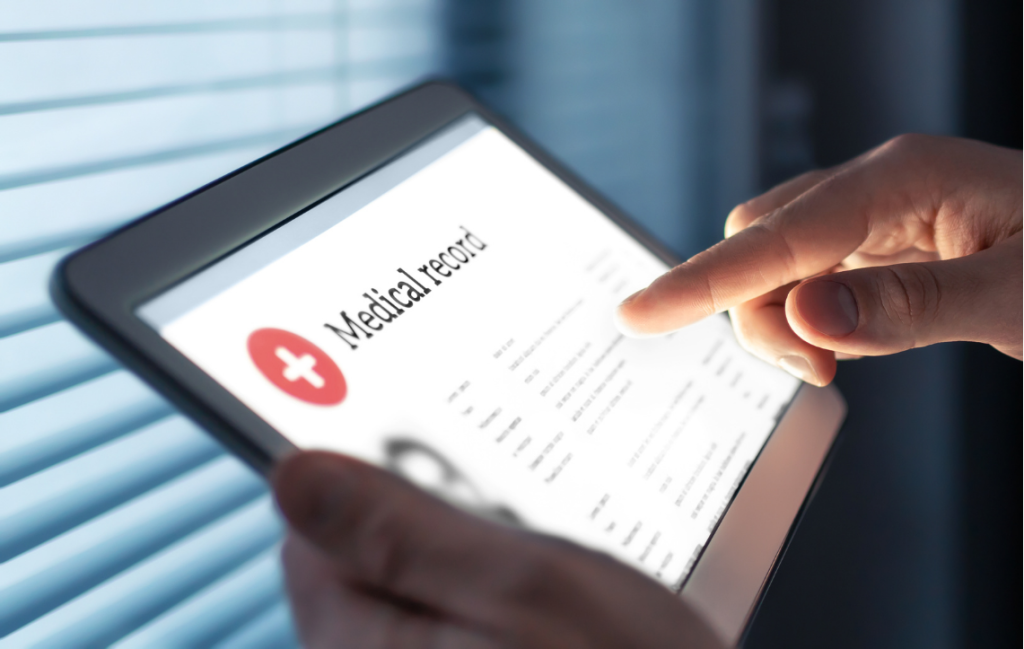
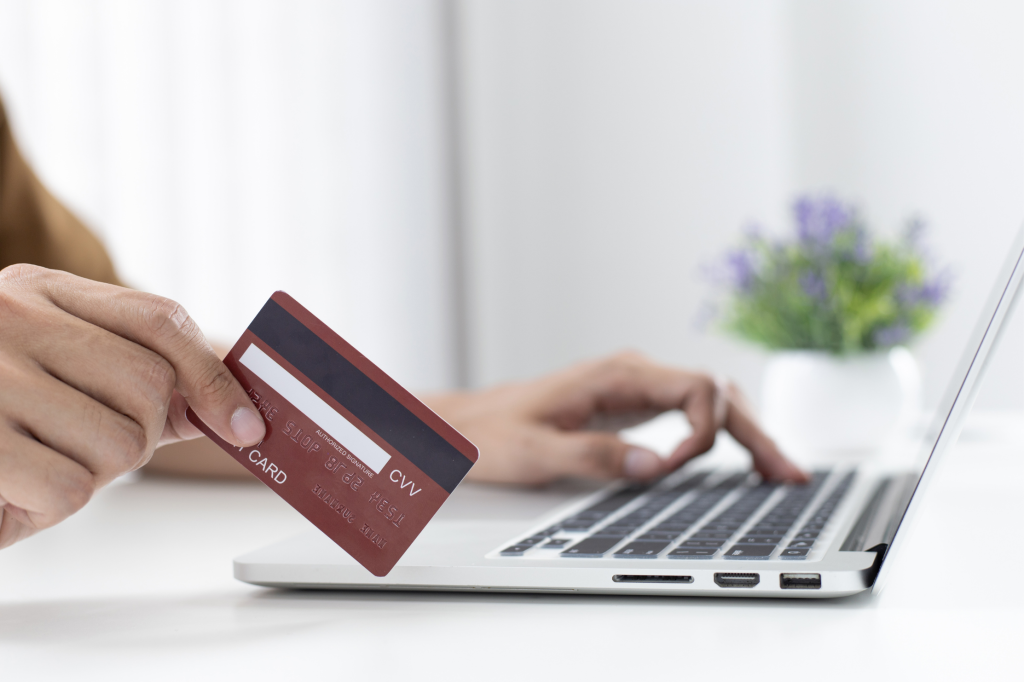
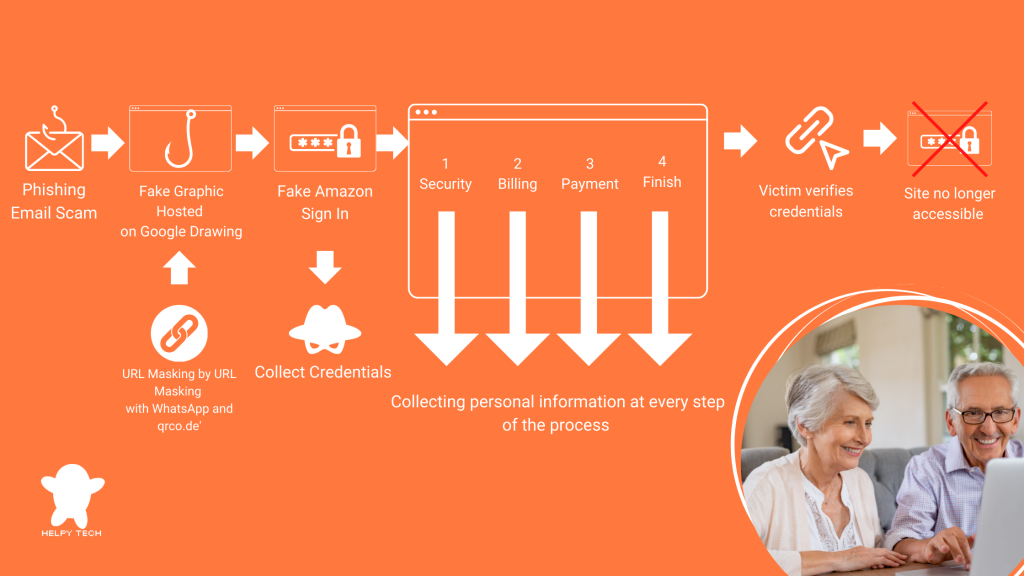
As more than 50% of seniors increasingly turn to online shopping, their strong reliance on trusted brands like Amazon has made them particularly vulnerable to a new and sophisticated phishing scam Understanding LOTS: How Scammers Exploit Trusted Sites with Amazon Phishing Emails List of Living Off Trusted Sites (LOTS) Ashwin Vamsh, an expert in cybersecurity, explains that this new Amazon phishing email scam exploits a tactic known as Living Off Trusted Sites (LOTS), where scammers use reputable and trusted websites to host their malicious content. By leveraging the trust users place in these well-known platforms, the scam becomes much harder to detect, making it especially dangerous for unsuspecting victims. Google Drawings: A Trusted Tool Used Maliciously In this case, the scammers are leveraging Google Drawings and WhatsApp’s URL shortener to mimic an Amazon confirmation site to carry out their attack.Google Drawings is a tool within the Google Workspace suite that allows users to create and share visual content. It’s typically used for collaborative projects, diagrams, or simple graphics. It also allow for embedding links into the drawings as well. However, in this scam, Google Drawings is being used to host a fake Amazon account verification graphic. Step-by-Step Breakdown: How the Amazon Phishing Email Scam Targets Victims Diagram of step-by-step Google Drawing Phishing Scam The Amazon phishing email scam begins with an email sent to the victim, prompting them to confirm their Amazon account. The email contains a link that appears legitimate but actually directs the user to a Google Drawing hosted on Google’s servers. Since the link is from Google, a trusted source, it easily bypasses most security filters and raises no immediate red flags for the user.To further deceive the victim and evade detection, scammers use a WhatsApp URL shortener, which is less likely to trigger security warnings. They then add another layer of obfuscation by re-shortening the link with a service like qrco.de, making it even harder to trace the original destination.Once the user clicks on the link in the Google Drawing, they are taken to a website that closely resembles the official Amazon login page, prompting them to enter their credentials. After logging in, the user is then guided through a multi-step process that mimics a legitimate Amazon verification, including: Scam steps on a fake Amazon site to collect personal info via fake login, verification, and payment pages. Security: Verifying personal information such as your date of birth, phone number, and mother’s maiden name. Billing: Confirming your billing address. Payment: Entering your credit card information. Finish: Completing the verification process. Even if the user becomes suspicious and stops midway, the damage may already be done, as scammers collect information at every step. Why the Amazon Phishing Email Scam is Dangerous for Older Adults For seniors who love shopping online, this kind of Amazon phishing email scam can be particularly dangerous. Many older adults have built a relationship of trust with brands like Google, Amazon, and WhatsApp over the years, making them more likely to fall for a scam that exploits these trusted platforms. The combination of familiar branding and a convincing interface makes it incredibly challenging to distinguish between legitimate and fake websites.Given the increasing sophistication of scams that use LOTS tactics, it’s crucial to take steps to protect yourself: Double-Check Links: Before clicking on any link, hover over it to see the full URL. If it looks suspicious or unfamiliar, don’t click it. Verify Directly with the Source: If you receive an email asking you to confirm your account or provide personal information, contact the company directly through their official website or customer service number to verify the request. Be Wary of URL Shorteners: Be cautious of links that use URL shorteners, especially from unfamiliar sources. These can be used to hide malicious sites. Use Security Software: Make sure your computer and devices have up-to-date security software that can help detect and block phishing attempts. Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest scams and tactics used by cybercriminals. The more you know, the better equipped you’ll be to recognize and avoid scams. Our Mission Helpy Tech’s mission is to help older adults stay informed and healthy through continuous education. As part of our scam prevention series, we are committed to providing the tools and knowledge needed to protect themselves. If you’ve ever been scammed, we would love to hear about your experience, comment it below!